Breathe Better, Live Stronger: Physiotherapy Strategies for Respiratory Wellness
Physiotherapy Post | Vol. 3, Issue 74 | April 2025
Dear Readers,
Welcome to this edition of Physiotherapy Post!
Big News for the Physiotherapy Community!
The National Commission for Allied and Healthcare Professions (NCAHP) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW), India has officially released a new, upgraded curriculum for Allied and Healthcare Sciences, including Physiotherapy!
This progressive curriculum is designed to align with international standards, emphasizing advanced clinical skills, research orientation, technology integration, and patient-centered care. It marks a major leap toward strengthening healthcare education and ensuring better career pathways for future professionals.
Stay tuned as we break down what this means for physiotherapy education, training, and practice in our upcoming editions!
Coming to our this week topic: Breathing — something so natural yet so powerful — forms the very essence of life. In this issue, we explore how physiotherapy interventions can significantly enhance respiratory wellness. From breathing exercises and airway clearance techniques to posture optimization and pulmonary rehabilitation, physiotherapists play a crucial role in helping individuals breathe better and live stronger.
Whether managing chronic respiratory conditions like COPD and asthma, supporting post-COVID recovery, or optimizing overall lung health, physiotherapy offers effective, evidence-based strategies to empower patients and improve quality of life.
Join us as we unlock the true potential of breath — and discover how small changes in breathing can lead to profound transformations in strength, endurance, and vitality.
Stay inspired, stay strong!
Dr. Aditi Singh
Editor-in-Chief, Physiotherapy Post
Respiratory health is foundational to human vitality, yet it is often compromised by conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, bronchiectasis, post-COVID lung dysfunction, and neuromuscular disorders. Physiotherapists play a vital role in optimizing respiratory mechanics, enhancing ventilation, and promoting overall wellbeing through structured, evidence-based interventions.
The Physiotherapy Approach to Respiratory Wellness
1. Breathing Retraining Techniques
Breathing retraining aims to correct dysfunctional breathing patterns that often develop in respiratory diseases.
Diaphragmatic Breathing: Encourages the use of the diaphragm rather than accessory muscles, improving oxygen exchange efficiency (Borge et al., 2015).
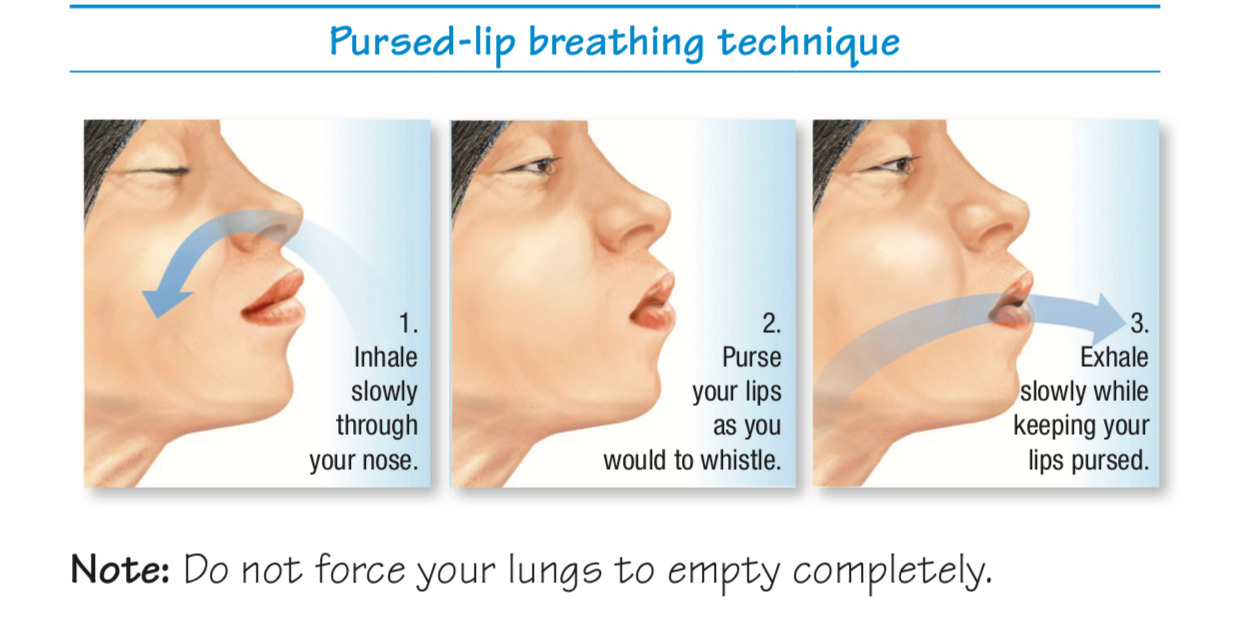
Pursed-Lip Breathing: Useful for patients with COPD; helps prevent airway collapse during exhalation and improves gas exchange.
Segmental Breathing: Targets ventilation to specific lung segments to improve localized oxygenation, especially post-surgery or in localized lung pathology.
Evidence: A meta-analysis by Hamasaki (2020) found breathing exercises significantly improved dyspnea and exercise tolerance in COPD patients.
2. Airway Clearance Techniques
Clearing secretions is crucial to preventing infection, improving ventilation, and maintaining airway patency.
Active Cycle of Breathing Technique (ACBT): A series of breathing control, thoracic expansion exercises, and forced expiratory techniques (huffing) shown to be highly effective in cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis (Pryor et al., 2010).
Postural Drainage: Positioning patients to use gravity to assist drainage from specific lung segments.
Oscillatory Positive Expiratory Pressure (OPEP) Devices: Devices like Flutter® and Acapella® create vibrations that loosen mucus, improving expectoration.
Evidence: Systematic reviews indicate OPEP therapy reduces exacerbations and improves lung function in COPD and bronchiectasis (Lee et al., 2013).
3. Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs
A multidisciplinary intervention combining exercise training, education, and behavior change aimed at improving the physical and psychological condition of people with chronic respiratory diseases.
Components: Aerobic training, resistance exercises, breathing exercises, and education sessions.
Duration: Typically 6–12 weeks, supervised by a physiotherapist.
Evidence: According to the American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society guidelines, pulmonary rehabilitation significantly improves dyspnea, exercise capacity, and health-related quality of life (Spruit et al., 2013).
4. Posture Correction and Thoracic Mobility
Thoracic cage stiffness and postural dysfunction, especially kyphosis, can impair ventilation.
Physiotherapy Interventions: Stretching tight muscles (pectorals, intercostals), strengthening postural muscles (trapezius, rhomboids), and mobilizing thoracic spine joints.
Evidence: Research shows that correcting forward head posture and thoracic kyphosis can improve lung volumes and peak expiratory flow (Katzman et al., 2017).
5. Inspiratory Muscle Training (IMT)
Strengthening the diaphragm and intercostal muscles through resistance breathing exercises.
Methods: Use of threshold devices like POWERbreathe®.
Indications: COPD, heart failure, athletes looking to boost performance.
Evidence: IMT improves inspiratory muscle strength, reduces dyspnea, and enhances exercise tolerance, particularly in moderate-to-severe COPD (Illi et al., 2012).
The Emerging Role of Physiotherapy Post-COVID
COVID-19 survivors often experience persistent pulmonary symptoms, reduced exercise tolerance, and psychological sequelae (e.g., anxiety related to breathlessness).
Early Mobilization
Breathing Exercises
Gradual Return-to-Exercise Programs
Evidence: A 2021 study in Respiratory Medicine demonstrated that structured pulmonary rehabilitation post-COVID led to significant improvement in 6-minute walk test results and quality of life scores (Abodonya et al., 2021).
News update:
1. Consumption of a diet high in fat and sugar is associated with worse spatial navigation ability in a virtual environment
Read more at: Link
2. Interview | Community participation and digital innovation vital for universal immunisation: UNDP India chief
Read more at: Link
Advanced methods transforming coronary artery treatments: Sr cardiologist
Read more at: Link
Upcoming event/s:
Thought of the Week:
If you have any questions or would like more personalised advice, feel free to reach out to our expert team at dr.aditisingh05@gmail.com.
Wishing you a vibrant and pain-free times ahead!
Warm regards,
Team Physiotherapy Post